Salvo Rinzivillo

Research Line 3 - leader
Involved in the research line 1 ▪ 3 ▪ 4 ▪ 5
Role: Researcher
Affiliation: ISTI - CNR Pisa
8.
[BGG2023]Francesco Bodria, Fosca Giannotti, Riccardo Guidotti, Francesca Naretto, Dino Pedreschi, Salvatore Rinzivillo (2023) - Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery
Abstract
The rise of sophisticated black-box machine learning models in Artificial Intelligence systems has prompted the need for explanation methods that reveal how these models work in an understandable way to users and decision makers. Unsurprisingly, the state-of-the-art exhibits currently a plethora of explainers providing many different types of explanations. With the aim of providing a compass for researchers and practitioners, this paper proposes a categorization of explanation methods from the perspective of the type of explanation they return, also considering the different input data formats. The paper accounts for the most representative explainers to date, also discussing similarities and discrepancies of returned explanations through their visual appearance. A companion website to the paper is provided as a continuous update to new explainers as they appear. Moreover, a subset of the most robust and widely adopted explainers, are benchmarked with respect to a repertoire of quantitative metrics.
9.
[MBG2023]Carlo Metta, Andrea Beretta, Riccardo Guidotti, Yuan Yin, Patrick Gallinari, Salvatore Rinzivillo, Fosca Giannotti (2023) - Springer Nature. In International Journal of Data Science and Analytics
Abstract
A key issue in critical contexts such as medical diagnosis is the interpretability of the deep learning models adopted in decision-making systems. Research in eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) is trying to solve this issue. However, often XAI approaches are only tested on generalist classifier and do not represent realistic problems such as those of medical diagnosis. In this paper, we aim at improving the trust and confidence of users towards automatic AI decision systems in the field of medical skin lesion diagnosis by customizing an existing XAI approach for explaining an AI model able to recognize different types of skin lesions. The explanation is generated through the use of synthetic exemplar and counter-exemplar images of skin lesions and our contribution offers the practitioner a way to highlight the crucial traits responsible for the classification decision. A validation survey with domain experts, beginners, and unskilled people shows that the use of explanations improves trust and confidence in the automatic decision system. Also, an analysis of the latent space adopted by the explainer unveils that some of the most frequent skin lesion classes are distinctly separated. This phenomenon may stem from the intrinsic characteristics of each class and may help resolve common misclassifications made by human experts.
26.
[BRF2022]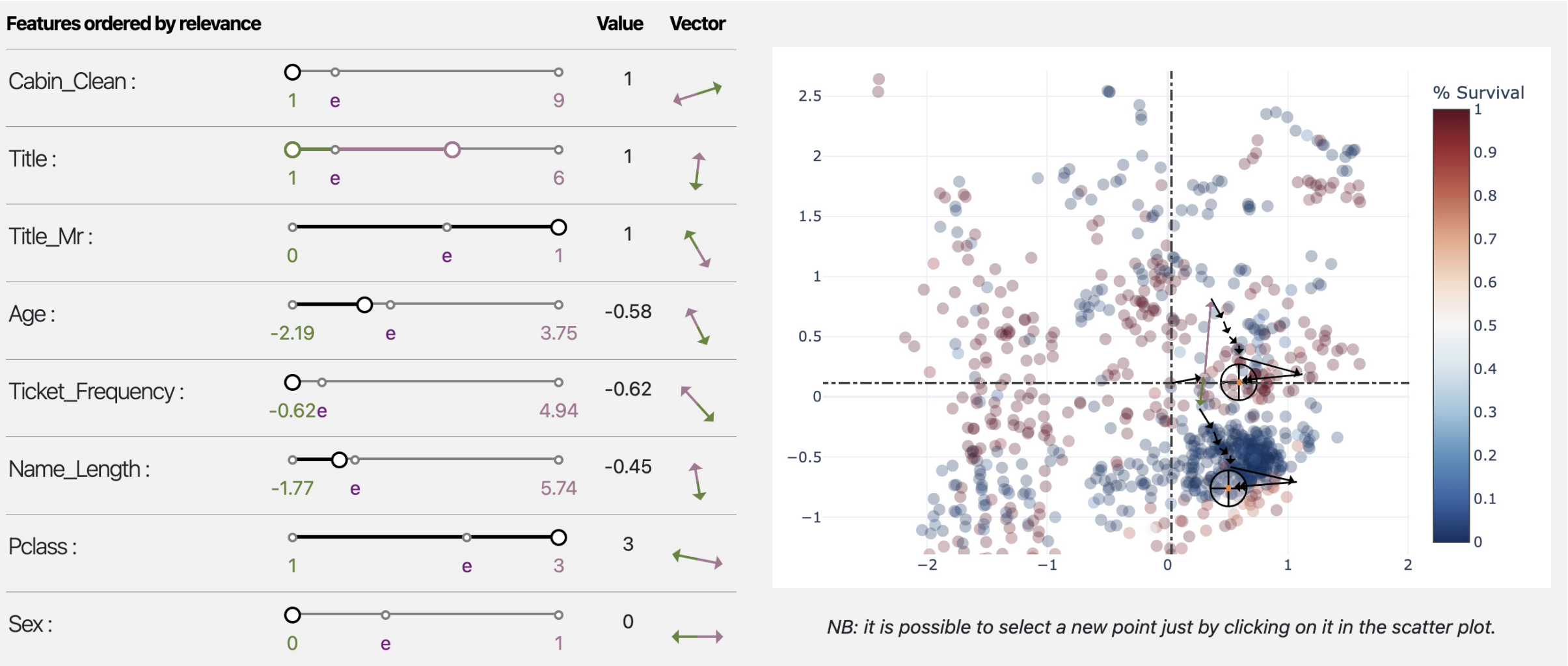
Bodria Francesco, Rinzivillo Salvatore, Fadda Daniele, Guidotti Riccardo, Fosca Giannotti, Pedreschi Dino (2022) - EUROVIS 2022. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference Eurovis 2022
Abstract
Autoencoders are a powerful yet opaque feature reduction technique, on top of which we propose a novel way for the joint visual exploration of both latent and real space. By interactively exploiting the mapping between latent and real features, it is possible to unveil the meaning of latent features while providing deeper insight into the original variables. To achieve this goal, we exploit and re-adapt existing approaches from eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) to understand the relationships between the input and latent features. The uncovered relationships between input features and latent ones allow the user to understand the data structure concerning external variables such as the predictions of a classification model. We developed an interactive framework that visually explores the latent space and allows the user to understand the relationships of the input features with model prediction.
27.
[PBF2022]Panigutti Cecilia, Beretta Andrea, Fadda Daniele , Giannotti Fosca, Pedreschi Dino, Perotti Alan, Rinzivillo Salvatore (2022). In ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems
Abstract
eXplainable AI (XAI) involves two intertwined but separate challenges: the development of techniques to extract explanations from black-box AI models, and the way such explanations are presented to users, i.e., the explanation user interface. Despite its importance, the second aspect has received limited attention so far in the literature. Effective AI explanation interfaces are fundamental for allowing human decision-makers to take advantage and oversee high-risk AI systems effectively. Following an iterative design approach, we present the first cycle of prototyping-testing-redesigning of an explainable AI technique, and its explanation user interface for clinical Decision Support Systems (DSS). We first present an XAI technique that meets the technical requirements of the healthcare domain: sequential, ontology-linked patient data, and multi-label classification tasks. We demonstrate its applicability to explain a clinical DSS, and we design a first prototype of an explanation user interface. Next, we test such a prototype with healthcare providers and collect their feedback, with a two-fold outcome: first, we obtain evidence that explanations increase users' trust in the XAI system, and second, we obtain useful insights on the perceived deficiencies of their interaction with the system, so that we can re-design a better, more human-centered explanation interface.
Research Line 1▪3▪4
33.
[MGY2021]Carlo Metta, Riccardo Guidotti, Yuan Yin, Patrick Gallinari, Salvatore Rinzivillo (2021) - IOS Press. In HHAI2022: Augmenting Human Intellect, S. Schlobach et al. (Eds.)
Abstract
Explainable AI consists in developing models allowing interaction between decision systems and humans by making the decisions understandable. We propose a case study for skin lesion diagnosis showing how it is possible to provide explanations of the decisions of deep neural network trained to label skin lesions.
39.
[MGY2021]Metta Carlo, Guidotti Riccardo, Yin Yuan, Gallinari Patrick, Rinzivillo Salvatore (2021) - 2021 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC). In 2021 IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications (ISCC)
Abstract
Explainable AI consists in developing mechanisms allowing for an interaction between decision systems and humans by making the decisions of the formers understandable. This is particularly important in sensitive contexts like in the medical domain. We propose a use case study, for skin lesion diagnosis, illustrating how it is possible to provide the practitioner with explanations on the decisions of a state of the art deep neural network classifier trained to characterize skin lesions from examples. Our framework consists of a trained classifier onto which an explanation module operates. The latter is able to offer the practitioner exemplars and counterexemplars for the classification diagnosis thus allowing the physician to interact with the automatic diagnosis system. The exemplars are generated via an adversarial autoencoder. We illustrate the behavior of the system on representative examples.
41.
[MBG2021]Metta Carlo, Beretta Andrea, Guidotti Riccardo, Yin Yuan, Gallinari Patrick, Rinzivillo Salvatore, Giannotti Fosca (2021) - Arxive preprint. In International Journal of Data Science and Analytics
Abstract
A key issue in critical contexts such as medical diagnosis is the interpretability of the deep learning models adopted in decision-making systems. Research in eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) is trying to solve this issue. However, often XAI approaches are only tested on generalist classifier and do not represent realistic problems such as those of medical diagnosis. In this paper, we analyze a case study on skin lesion images where we customize an existing XAI approach for explaining a deep learning model able to recognize different types of skin lesions. The explanation is formed by synthetic exemplar and counter-exemplar images of skin lesion and offers the practitioner a way to highlight the crucial traits responsible for the classification decision. A survey conducted with domain experts, beginners and unskilled people proof that the usage of explanations increases the trust and confidence in the automatic decision system. Also, an analysis of the latent space adopted by the explainer unveils that some of the most frequent skin lesion classes are distinctly separated. This phenomenon could derive from the intrinsic characteristics of each class and, hopefully, can provide support in the resolution of the most frequent misclassifications by human experts.